Unlike their 1D counterparts, 2D barcodes offer significant increases in data capacity and functionality. They have revolutionized inventory management, product tracking, mobile payments, marketing campaigns and more.

What is a 2D Barcode and How Does It Work?
A 2D barcode is a visual representation of data that can be scanned and decoded. It is also known as a two-dimensional barcode. This type of barcode can be read using a barcode reader or a mobile device with a camera.
2D codes can store more data in a smaller space compared to 1D barcodes. They use patterns of squares, dots, hexagons, or other shapes.
2D barcodes encode data both horizontally and vertically, allowing them to store alphanumeric characters, binary data, and even images or website URLs. They are commonly used to track products, facilitate mobile payments, store contact information, and provide easy access to online content.
Is a 2D Barcode the Same as a QR Code?
A 2D barcode and a QR code are not exactly the same, although a QR (Quick Response) code is a specific type of 2D barcode. While all QR codes are 2D codes, not all 2D codes are QR codes. QR codes are often used for many things like ads, tracking products, paying with your phone, and connecting to websites. They can store different type of information such as text, URLs, contact details, etc.
What are the Types of 2D Barcodes?
There are several types of 2D barcodes, each with its own specific features, data capacity, and areas of application including:
- QR (Quick Response) Code - they consist of black squares arranged on a white background, typically in a square or rectangular shape and can store various types of data.
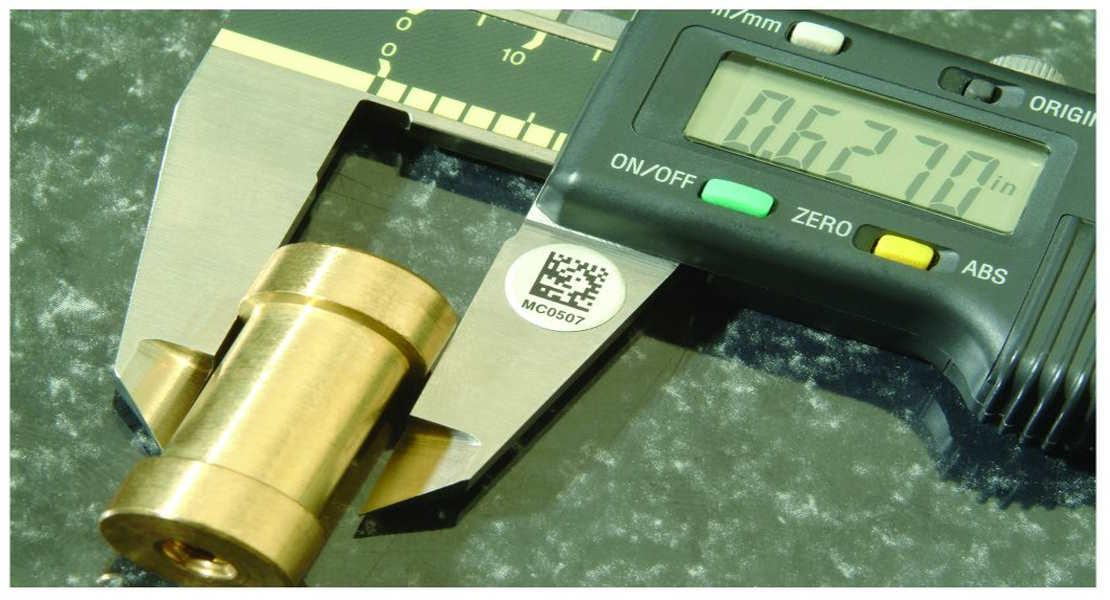
- 2D Data Matrix Code - they are compact and can store a large amount of data in a small space. They consist of black and white square or dots arranged in a square or rectangular grid. 2D Data Matrix codes are used in IUID.
- PDF417 - they can store a significant amount of data, including text, numbers, and binary information. They consist of stacked rows of black and white bars, with each row capable of storing multiple characters.
- Aztec Code - they are high density 2D codes that can encode large amounts of data and are often used for mobile ticketing, transportation systems, and applications requiring compact codes.
What are the Benefits of 2D Barcodes?
2D barcodes offer numerous advantages over traditional 1D barcodes. Firstly, they can store significantly more data, including text, numbers, and even small images, making them more versatile for various applications such as inventory management, ticketing, and product tracking. Secondly, they are more resistant to damage and distortion, ensuring reliable scanning even when printed on curved or uneven surfaces.
Moreover, 2D barcodes support error correction, meaning they can still be decoded accurately even if part of the code is obscured or damaged. This robustness enhances efficiency and reduces errors in data capture processes.
Lastly, the widespread use of smartphones with built-in cameras has made 2D barcodes easily accessible, enabling seamless integration into mobile apps for tasks like mobile payments, digital loyalty programs, and boarding passes, further expanding their utility and convenience.
What is the Difference Between 1D and 2D Barcodes?
There are a number of key differences between 1D and 2D barcodes. 1D barcodes consist of a sequence of parallel lines of varying thickness and spacing. In contrast, 2D barcodes utilize patterns of squares, dots, hexagons, or other shapes to encode information both horizontally and vertically.
2D codes have a significantly higher data capacity compared to 1D barcodes. The amount of data 2D barcodes can store ranges from a few hundred characters to several kilobytes.
1D barcodes primarily contain numeric data and basic text information while 2D barcodes can encode various types of data, including text, numbers, contact details, URLs, and multimedia content. 1D barcodes require a barcode reader for scanning. 2D barcodes, on the other hand, can be scanned using special barcode scanners or mobile devices equipped with cameras.
Metalcraft offers both 1D and 2D barcodes in all our barcode product offerings including best-selling Metal Barcode Nameplates and Foil Barcode Labels as well as our Premium Polyester Barcode Labels and other roll label products.
How do 2D scanners work?
2D scanners work by capturing an image of the entire barcode, rather than scanning it line by line like 1D scanners. These scanners typically use a combination of image sensors, lenses, and light sources to capture a high-resolution image of the barcode.
Once the image is captured, specialized software processes it to decode the barcode's data. Decoding a barcode means identifying the specific patterns and shapes in the image. These patterns and shapes are then translated into the corresponding information. Advanced algorithms are often employed to handle various types of 2D barcodes and to compensate for factors like distortion, damage, or poor lighting conditions, ensuring accurate and reliable scanning.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of 2D scanners?
2D scanners offer several advantages over their 1D counterparts. Firstly, they can store significantly more data, enabling them to encode not only alphanumeric characters but also images, URLs, and other types of information. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from inventory management to mobile payments.
Secondly, 2D scanners are more robust when it comes to scanning damaged or obscured barcodes. Their ability to capture the entire barcode image means they can still decode the data even if parts of the code are missing or damaged. Additionally, 2D scanners are often integrated with smartphones and other mobile devices, allowing for easy and convenient scanning on the go.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider. One drawback is that 2D scanners can be more expensive and complex than 1D scanners due to the additional hardware and software required to capture and process the barcode images. Additionally, the larger size of 2D barcodes may make them unsuitable for certain applications where space is limited. Finally, while 2D barcodes offer increased data capacity and versatility, they may not be necessary for every application, and in some cases, a simpler 1D barcode may suffice. Overall, the choice between 1D and 2D scanners depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application in question.
In summary, 2D barcodes are a popular choice for various applications due to their smaller size, ability to encode more information and the ability of using a smart phone or other mobile device to scan than their 1D barcode counterpart. For more information on 2D barcodes or to receive FREE samples, contact us at [email protected] or 800-437-5283.
 | About the Author: Marianne AlvaradoMarianne Alvarado is our Vice President of Sales. Alvarado joined Metalcraft in March of 2000 as a Territory Specialist, became Sales Manager in January 2022 and was named Vice President of Sales during August of 2023. She leads both the Outside and Inside Sales teams. Marianne lives in Davenport with her husband, Dave Beeman. Mobile Phone: 641-529-9492 Email: [email protected] Office: 3360 9th St. SW, Mason City, IA 50401 Office Phone: 641-423-9460 |